![[LWN Logo]](http://old.lwn.net/images/lcorner.png)
![[LWN.net]](http://old.lwn.net/images/bigpage.png)
![[LWN Logo]](http://old.lwn.net/images/lcorner.png) |
![[LWN.net]](http://old.lwn.net/images/bigpage.png) |
Bringing you the latest news from the Linux World.
Dedicated to keeping Linux users up-to-date, with concise
news for all interests
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page
Other LWN stuff:
Archives/search
Recent features: Here is the permanent site for this page. See also: last week's LWN.
|
Leading items and editorialsLinux: a Ben and Jerry's or Amazon business? For those who have not yet read it, we strongly recommend a look at this "strategy letter" by Joel Spolsky. It divides startup businesses into two broad categories, each named after a company that epitomizes it:
Obviously the two different types of companies are two very different places to be, though each has its advantages. Beyond that, however, the author makes two points about these company models that are worth some consideration. First is that every company has to choose one or the other and be serious about it. Attempts to mix the two approaches will fail. The other is that the market the company is in can determine which model will be successful. Land grabs can be called for when there are large network effects, and there is little competition in the area already. The Ben and Jerry's model makes more sense when competition exists, and customer lock-in is relatively weak. Amazon had to grab the turf before somebody else did, while Ben and Jerry's could not have done an ice cream land grab whether it wanted to or not. So how do these models apply to the business of Linux? Until sometime around 1998, Linux companies all followed the Ben and Jerry's model, for the simple reason that the funding for aggressive growth did not exist. Companies like Red Hat, SuSE, VA Linux, LinuxMall.com, and others grew slowly for years as Linux slowly caught on. Much of that has changed over the last two years, as funding for Amazon-type companies became available. Now, it seems, being a proper Linux company requires regular acquisitions, constant growth, and wild expenditures of cash. Lineo, currently in the IPO process, is a classic example of the new type of Linux company. By way of no less than six acquisitions, it has sought to gain both size and market share as quickly as possible. Most other high-profile Linux companies are also operating in the Amazon mode. But is that the way that Linux businesses should work? Land grabs work when there are strong network and lock-in effects. Linux does have the usual network effects associated with operating systems - every user who adopts Linux makes your Linux system worth more. But this effect is truly a tide that lifts all boats, because lock-in with Linux is nearly absent. That is, after all, one of the advantages of Linux. Changing from one distributor or support provider to another may not be entirely fun, but it is not that big a deal, either. Thus territory occupied by land grabs is going to be very hard to defend. Massive marketing budgets and acquisitions may well succeed in getting customers, but those same customers will head for the door quickly if they are not happy with what they find - they have many other alternatives. When you use Linux, you are not locked in to any vendor. Linux itself has grown in the Ben and Jerry's mode - slowly, patiently, and without the ability to "acquire" market share. It may well be that the most successful Linux businesses, in the end, operate in the same way. The model for these businesses may not be a corporation at all; it may, instead, be the Debian project. Debian continues to grow in users and developers both, despite its publicly-traded competition. Wouldn't it be interesting if the Linux business model that found the most success in the long term were based on some variant of Debian's constitutionally-driven cooperative, distributed setup? Oracle's "Internet appliance" system is out. The "New Internet Computer" (NIC) is the latest result of Larry Ellison's long personal crusade to make non-Microsoft systems available to the world. It's aimed at people who only want access to the net; as such, it's essentially a $199 (without monitor) X terminal. It has a 266 MHz processor, 64MB of memory, Ethernet and USB ports, a CDROM, and a built-in modem. And, of course, a Linux operating system. (Some) more information may be found in the press release. What it doesn't have is a hard drive. The NIC boots directly from CD, and the entire system is to be found there. A bit of flash memory is provided for the saving of bookmarks (and, presumably, cookies); otherwise the system is completely read-only. The creation of a "no maintenance" system makes a lot of sense for the intended audience. One wonders, though, what will happen when the first nasty, remotely-exploitable security hole in the NIC is found. Will Oracle ship new CDs to every customer? Even if the company were willing to take on that expense, how quickly could that distribution be done? One can hope that the NIC has been configured with security in mind, but, even so, the possibility of widespread, unfixable security problems is a bit worrisome. The CD-based nature of the system also makes customization difficult in general. Fortunately, the architecture of the NIC is more open than, say, the iOpener. If the device is successful, one can expect to see a wide market in value-added replacement OS disks. One could imagine creating NICs oriented toward a number of dedicated tasks, from recipe management to point-of-sale or factory floor applications. It is far too early to say whether the NIC will be a successful product. The network appliance market is still unformed and untested, after all. But this system shows, perhaps, how Linux may take over the desktop - and countertop - after all. Software Patents Still on European Commission Agenda. EuroLinux has issued this update warning that the European Commission agenda still includes the topic of software patents. Whatever your opinion on this matter, be aware that following the issue and making sure you have an opportunity to voice your opinion before a decision is made is important. "The General Directorate for Internal Market at the European Commission has not changed its ideologic position in favour of software patents." A wealth of conferences is on tap for next week. The O'Reilly Open Source Software Convention is happening July 17 to 20 in Monterey, California; LWN's Dennis Tenney will be attending, and we hope to have contributed reports from another attendee. Those interested in hard-core hacking, however, will be heading north to the Ottawa Linux Symposium, held July 19 to 22. LWN editor Jon Corbet plans to be there, if some last-minute complications don't get in the way. The Ottawa event, limited to 500 attendees, sold out on June 23. Inside this week's Linux Weekly News:
This Week's LWN was brought to you by:
|
July 13, 2000
|
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Security page. |
News and EditorialsSSH 1.2.30 released, new restrictive license. Since we published last week's Security Summary, two new versions of SSH 1.2.X have been released, 1.2.29 and 1.2.30. Both of these newer versions include bug-fixes, some of them security-related. In addition, though, as a kicker, both of the new versions have an updated license, directly taken from the ssh 2.X series. The license for ssh 1.X and 2.X has never been totally free, but the original 1.X license allowed both commercial and non-commercial uses in most cases. As of this point, anyone wanting to continue to use the ssh 1.X series will probably need to purchase a commercial license in order to do so (student and faculty members using it for non-commercial or charitable purposes are excepted). When we posted the above item on the LWN Daily Page earlier this week, we also pointed out the availability of OpenSSH, a free software alternative to SSH from the folks at OpenBSD. OpenSSH supports both the ssh 1 and ssh2 protocols. It seems likely that many people who haven't bothered to move from ssh to openssh, if only because of inertia, may decide to do so now that SSH Communications has decided to further restrict their licensing.
We must, however, include one caveat, courtesy of Dave Finton,
who pushed us to investigate potential patent issues with
OpenSSH. Although OpenSSH itself
is a free software product, openssh 1.X does use the patented RSA
algorithm, which could get a commercial company into trouble, if they
choose to move to it:
ZDNet calls this outcome a Cinderella story, not just because OpenSSH was created as a free alternative to SSH, but because the project was already fully-developed and available to replace SSH Communication's ssh, the minute they chose to restrict their license too far. "The moral of this tale? Next time you encounter a piece of software whose license is too restrictive for your tastes, don't get mad; do what the OpenSSH project did and get even!"
For even more fun, check out the feedback on the above ZDNet article.
One respondent compared the situation to another several years ago:
Rain Forest Puppy's White Paper. In last week's Security Summary, we link to a ZDNet article that discusses a white paper from Rain Forest Puppy on proposed guidelines for researchers and vendors dealing with security issues. The ZDNet article did not provide a URL for RFP's white paper, which is available at http://www.wiretrip.net/rfp/policy.html. (Thanks to Alex Butcher, Brent J. Nordquist and others). Openhack-interactive security redux (eWeek/ZDNet). eWeek/ZDNet promotes OpenHack, its current challenge/contest to hackers to break into a set of preconfigured systems. "Some in the industry say that hacking contests are just publicity stunts, positing that, since the typical prize money is so small, no hacker worth his or her salt would want to participate. My view is more practical. Hackers who deface Web sites aren't in it for the money. They may not even be in it for the publicity. They do it because they can." Security Reports/tmp vulnerabilities in XFree86 4.0.1. Joseph S. Myers reported a /tmp vulnerability in the installation program for XFree86 4.0.1, commenting that he had previously reported the same problem for XFree86 4.0 in March and that other such errors could be found elsewhere in XFree86. BugTraq ID 1430 gives a concise list of the vulnerabilities he has reported. No comment has been seen from the XFree86 development team as of yet, nor any distribution updates. XFree86 4.0 local root vulnerability. FreeBSD has issued an advisory regarding a vulnerability in XFree86 4.0 that can be exploited by a local user to get root access. They provide updated packages but also discourage the installation of XFree86 4.X on multi-user systems with untrusted local users. They also indicated that XFree86 4.0.1 most likely contains a fix for this problem. BitchX format bug. BitchX, a popular IRC client, contains an exploitable formatting error, both in 1.0c16 and 75p3. An exploit can take the client down remotely. Patches for both versions have been made available.
ftp setproctitle() vulnerability. A format string vulnerability in setproctitle() impacts multiple versions of ftp, including proftpd, wu-ftpd, FreeBSD, NetBSD and OpenBSD. An upgrade to proftpd 1.2 and FreeBSD 2.2 or later will fix the problem for those platforms.
LPRng incorrect file permissions. LPRng author Patrick Powell posted an advisory reporting that LPRng 3.6.15 and earlier incorrectly installed by default suid root. He identified a manner in which the root privilege could be exploited and recommended that all users of LPRng remove the suid root permissions or upgrade to LPRng 3.6.20, in which the installation no longer assigns suid root. Note, however, that the removal of root permissions may break compatibility with the older lpr/lpd installations, according to Cy Schubert. tnef remote compromise. SuSE issued a security advisory regarding a vulnerability in tnef that could be remotely exploited to overwrite system files. tnet is a program that extracts mail packaged in Microsoft Outlook format. Updated packages are provided. FreeBSD: libedit. FreeBSD has issued an advisory for problems with the libedit library, where its use of a configuration file can be abused to cause a user of libedit to execute commands unknowingly. A patch for the problem is provided. CGI scripts. The following CGI scripts were reported to contain vulnerabilities: Commercial products. The following commercial products were reported to contain vulnerabilities: Updateswu-ftpd. Check the June 15th Security Summary for a link to the mini-audit that turned up the latest set of problems with wu-ftpd. wu-ftpd 2.6.1 contains fixes for this problem. Note that this is not the same problem as multiple vendor ftpd security report listed above.
man/makewhatis vulnerability. A /tmp file vulnerability has been found in makewhatis versions 1.5e and higher. Check last week's LWN Security Summary for the original report.This week's updates:
dump/restore. A security vulnerability in dump/restore has been fixed as of dump 0.4b18. Check the June 15th Security Summary for details.
canna. Check last week's Security Summary for more details. Buffer overflow in inn. A buffer overflow in inn 2.2.2 has been reported that can be an issue if the option "verifycancels" in /etc/news/inn.conf is set to "true". Setting this option to "false" should fix the problem.
ISC DHCP client. Check the June 29th Security Summary for more details. An upgrade to 2.0pl1 or 3.0b1pl14 should resolve the problem.
Qpopper. Check the May 25th Security Summary for more details. Qpopper 3.0.2 or later should fix this problem. OpenSSH. Check the June 15th Security Summary for details. Majordomo wrapper vulnerability. Check the June 1st Security Summary for the initial report. FreeBSD system call. FreeBSD has issued an updated advisory regarding a system call problem originally discussed in the June 1st Security Summary. ResourcesBastille Linux 1.1.1.pre2. A minor update to the Bastille Linux security hardening script has been made available, including bug fixes and improvements to the API library. Nessus 1.0.2. OpenBSD support has been added, as of this latest minor update to the Nessus security scanner. Secure-Linux Patch 2.2.16 version 1. The secure-linux patch has been updated to support the latest stable kernel, 2.2.16. PScan simple security scanner. In response to the growing number of reports of exploitable format string vulnerabilities, Alan DeKok announced PScan, a simple program that checks for potential format string problems in the source code. Building Internet Firewalls, second edition released. O'Reilly has announced the release of the second edition of "Building Internet Firewalls". "The second edition is much expanded. It covers Linux and Windows NT, as well as Unix platforms. It describes a variety of firewall technologies (packet filtering, proxying, network address translation, virtual private networks) as well as architectures (e.g., screening routers, dual-homed hosts, screened hosts, screened subnets, perimeter networks, internal firewalls)." Cybernotes (July 3rd). The July 3rd edition of Cybernotes, a publication from the National Infrastructure Protection Center (NIPC), is now available (PDF format). Cybernotes is published bi-weekly and produces a spread-sheet-like listing of reported vulnerabilities and affected operating systems. EventsJuly/August security events.
Section Editor: Liz Coolbaugh |
July 13, 2000
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Kernel page. |
Kernel developmentThe current development kernel release is 2.4.0-test3. This revision is a 4.5MB patch which touches over 1100 files and brings some significant changes. It contains a great many architecture-specific updates, including the addition of Cobalt Microserver support as a separate MIPS sub-architecture. There is the addition of a massive "ACPI interpreter" (it adds 120KB to a compiled kernel) which will someday make advanced power management capabilities available. The "memory technology device" driver has been integrated, bringing support for a great many "disk on chip" and flash memory devices; along with this support comes the Journaling Flash File System from Axis Communications. Also in this patch is an IEEE1394 ("firewire") update which includes new video support, an experimental USB Bluetooth driver, a Keyspan USB-to-serial driver, a reorganization of the USB storage driver, a major cleanup of the slab memory allocator, a reworking of the IP packet reassembly code, and the usual long list of little fixes. Here's the diffstat listing for those who want to see the full list of files changed by this patch. There is also a 2.4.0-test4 prepatch out there, currently in its fifth revision. This relatively small patch includes the addition of support for Orion boards as another MIPS sub-architecture, a big update to the Microgate SyncLink ISA and PCI serial adapter driver, more ACPI code work, and a number of other small tweaks. The current stable kernel release is still 2.2.16. The 2.2.17 prepatch is up to 2.2.17pre11, but there was no announcement for this revision. Alan does say that he hopes 2.2.17pre12 "or so" will be the final prepatch release. Latency, continued. The latency discussion continued to simmer slowly over the last week, in a more constructive mode. It may well be that a Linus-acceptable, low-latency patch will make it into the 2.4 kernel. Latency problems come about when the kernel code spends an excessively long time on one task, to the detriment of others. Thus all of the attempts to attack latency problems have come down to finding places where the kernel hogs the CPU for too long and breaking them up. In the end, a low-latency patch consists mostly of the addition of "rescheduling points," places where the code checks for other things to do and possibly allows another process to run. The addition of rescheduling points must be done with care, since the kernel is full of places where it is not prepared to be interrupted. It is also easy to get into the mode of tossing rescheduling points in everywhere, without really thinking about whether they are really needed or whether there is a better solution to the problem. Linus's objections to the current patches are based in a dislike of the shotgun approach to rescheduling points. A few, well thought-out points are acceptable; lots of them are not. Thus the current work is aimed at the insertion of a minimal number of these rescheduling points, and justifying each one well. Andrew Morton has taken on this task, and appears to have come up with some good results. He posted an initial patch which inserted six rescheduling points, and which reliably produced 4ms latency results as long as you avoided things on his "don't do that" list (included with the patch). He also made available a set of tools for measuring latencies. That patch drew a few complaints because one of the "don't do this" items was deleting large files - something that people who work with audio tend to do a lot of. That particular problem turned out to be solvable. The latest version of the patch is up to nine rescheduling points, and provides latencies of less than 1ms 99.999% of the time. Linus has not passed any (public) judgment on this patch, but it would appear to meet his criteria for an acceptable low-latency fix. It may well go in. Meanwhile, the long-term solution is likely to be different - the 2.5 development series will probably make kernel code preempt-able in most places. At that point, most of the code is automatically a rescheduling point, and the need to put them in explicitly will go away. (Roger Larsson has also updated his latency profiling patch). Memory management - the other performance problem. The current development kernels still have significant problems with memory management in some situations, leading to much worse performance than 2.2 in some situations. A number of kernel hackers are currently working on the problem, which is perhaps one of the biggest obstacles to the 2.4.0 release. The problems, unfortunately, are not something that can be fixed with a few small tweaks; it goes deeper than that. One thing that needs to be done, according to Stephen Tweedie, is to separate the tasks of taking memory away from a process and committing its contents to disk. The addition of this sort of "multiqueue" structure, being done by Rik van Riel, will make a lot of tasks easier; according to Stephen: "I really think we need to forget about tuning the 2.4 VM until we have such fundamental structures in place. Until we have done that hard work, we're fine-tuning a system which is ultimately fragile." In other words, it is going to be a while before Linux memory management is ready for 2.4.0. The 2.5 development series looks to be fun as well, since there seems to be a consensus that memory management needs to be thrown out and done over at that point. The Linux-USB mailing lists are moving. Have a look at this announcement to see how to make the transition and subscribe to the new lists. Other patches and updates released this week include:
Section Editor: Jonathan Corbet |
July 13, 2000 For other kernel news, see: Other resources: |
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Distributions page.
Lists of Distributions |
DistributionsPlease note that security updates from the various distributions are covered in the security section. New DistributionsIceLinux. IceLinux is a new distribution self-dubbed, "The Linux Gaming Platform of the future". Please note that the distribution is *so* new, that it hasn't actually been built yet. Nonetheless, the goal to build a distribution specifically as a gaming platform, to take a look at Linux's shortcomings in this arena and make it a priority to address them, is certainly admirable. Good luck! (Contributed from Ratatosk). Serial Terminal Linux. Another mini-distribution, Serial Terminal Linux is a single-floppy which contains minicom, allowing old computers and laptops to be used as serial terminals. The latest release allows support for multiple virtual consoles, one for each serial port on the computer. Minor updatesCaldera OpenLinuxNew FAQs. This week's new FAQs from Caldera includes tips on disabling module loading upon startup, an issue that is becoming of more interest lately for security reasons. Caldera Systems' OpenLinux Power Solutions Tour 2000. Caldera Systems has announced its "Power Solutions Tour 2000," starting July 11 in Toronto. The tour then moves to the U.S. with several stops in July. ConectivaConectiva receives investments. Conectiva has announced the receipt of investments from Intel Capital and LatinTech Capital. The amounts, of course, have not been disclosed. DebianReport from the Zeroth Debian Conference. Marcelo Magallon has written up a report from the Zeroth Debian Conference, which was held in Bordeaux, France, on July 5 to 9. It is a comprehensive and interesting summary, worth a read. Debian Weekly News (July 11th). This week's Debian Weekly News is available, with a brief summary and links from the Zeroth Debian Conference, an update on the upcoming test cycle 3 and apparently a pending decision to dump libc5 support from future Debian releases. Why we need Debian (ZDNet). Evan Leibovitch takes a moment to talk about why Debian is the most important Linux distribution. "In a world of NDA-bound business agreements, Debian is an open book. In a world of mission statements, Debian has a Social Contract. At a time when commercial distributors are striving to see how much proprietary software they can pack into a box of Linux, Debian remains the bastion of software freedom -- living proof that you can have a fully functional and usable operating system without needing any proprietary code." Libranet LinuxLibranet Linux available for download. The Libranet Linux distribution is now available for download. Libranet is a desktop-oriented distribution. It is described on the web page as "memberware" - one is supposed to sign up for a $10 membership to use the software (though the download is unrestricted). Linux-MandrakeLinux-Mandrake and MacMillan: good or bad for LM's future?. On the Linux-Mandrake forum, one reader/poster voiced his opinion that Linux-Mandrake made a mistake forming an exclusive relationship with MacMillan. "Macmillan is a big player, but they look like a newborn child in comparison with names like Ingram Micro , Tech Data, Gates/Arrow distributing, Merisel, and others .... who last year made billions of dollars in sales distributing "that other OS" (windows) and all parts that go in and out of a computer." The semi-official response? "Due to MacMillans distribution channels, Mandrake-Linux has been catapulted from 0 to 2nd best selling Linux distribution in less than a year! And we are heading full-spead towards being number one." Red HatRed Hat announces high availability server distribution. Red Hat has announced a new version of its distribution called "Red Hat High Availability Server 1.0". As might be expected, it's a clustering product, aimed at web server and other such applications; it includes failover and security features. It also includes a higher price tag: $1995. If you wish though, you can also download the software. News.com took a look at the new product. "As is customary with Red Hat, the software is open source, meaning it can be downloaded and modified for free. The $1,995 version, however, offers automated setup, detailed manuals, a more hacker-proof default installation, and a year of technical support, said spokeswoman Becky Mananich." We checked with Becky Mananich on the "more hacker-proof default installation" comment. She indicated that the High Availability Server currently incorporates all the security patches that have been released for Red Hat 6.2. In addition, the installation procedure, in comparison to Red Hat 6.2, offers a "cluster" option in which only the required components for clustering are installed and enabled, always a good choice for security. Slackware LinuxSlackware 7.1 Preview (GnuLinux.com). GnuLinux.com reviews the Slackware 7.1 beta. "In summary, there's not a huge change between 7.0 and 7.1 (not that we were expecting one), but everything that has changed has definitely changed for the better." Slackware Tools. A couple of Slackware tools were announced this week, including slackUp 1.0, an auto-upgrade program that can be used to keep your Slackware distribution in sync with the Slackware-current tree. Alternately, you can use it to upgrade a single package. Version 1.1 of the Slackware package manager was also announced this week. It supports packages in both rpm and .tgz format. SuSEPreliminary release of SuSE Linux for S/390. SuSE has announced the release of a preliminary version of its distribution for the IBM S/390 platform. SuSE Executive Interview (32BitsOnline). 32BitsOnline interviews Volker Wiegand, President of SuSE USA. "At this point we are observing the embedded market closely, but have no immediate plans to enter the market. We believe that embedded systems are still dominated more by hardware manufacturers, and Linux is only in its early stages there. Right now, we are building up the relevant expertise and are identifying opportunities." Reader Report: SuSE Linux (MacInTouch). The Mac community is taking a closer look at Linux, as demonstrated by this Reader Report on SuSE Linux in MacInTouch. "Summary: SuSE Linux is a very interesting UNIX alternative for those who don't have the money or hardware to use Mac OS X Server and can't wait for Mac OS X. It is perfect for a network server and the server tools included would cost hundreds of dollars on the Macintosh platform. Linux is also a great environment for programmers, it is probably less attractive as a desktop alternative to the Mac OS". [Editor note: this link works most of the time, but apparently not for everyone]. Yellow Dog LinuxTerra Soft to bundle RTLinux. Terra Soft Solutions has announced that the real-time Linux (RTLinux) patches will be integrated into future versions of the Black Lab Linux and Champion Server products. Embedded LinuxReport from the first Embedded Linux Expo & Conference
(LinuxDevices).
Rick Lehrbaum has issued his report
from the first Embedded Linux Expo, held June 22. "The ELEC
technical conference was completely sold out by the morning of the event,
resulting in "standing room only" during nearly all the presentations.
Likewise, all of the expo space was fully booked by product vendors,
producing an extremely vibrant Embedded Linux Expo that was bustling with
the enthusiasm of a rapidly expanding market. One pleasant surprise
was the international flavor of the event. Although most conference
participants were from the US, the following countries were also
represented: Armenia, Canada, England, Germany, Korea, China, South
Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, and the UK. Embedded Linux Consortium seats first board of directors. The Embedded Linux Consortium has announced the election of its first board of directors: Inder Singh, Michael Tiemann, James Ready, Tim Bird, Dan Bandera, and Greg Wright. Team takes different path to real-time Linux (EE Times). This EE Times article takes a look at RTLinux. " Dubbed RTLinux, the OS doesn't try to change Linux into an RTOS, but instead provides a homemade RTOS kernel that incorporates Linux as a low-priority thread. Thus the RTOS stays as small and streamlined as possible - a principal goal of RTLinux's creators - while retaining Linux as the basis for common applications." Group plans to launch Real Time Linux Consortium (LinuxDevices.com). Here's an article on LinuxDevices.com about plans to launch a real time Linux consortium at the second Real Time Linux Workshop in November. "The RTL community expressed their interest in a uniform and standardized API which they can rely on. Moreover, for most of them and especially for industry, the existence of such an API with a certain continuity and consistency guaranteed for a longer period, constitutes a basic requirement and condition for the use of RTL." e-smith Launches server 4.0. Last week, we mentioned e-smith 4.0b10. Apparently 10 betas was sufficient; e-smith has announced the release of version 4.0 of its Linux-based "server and gateway" product. TimeSys Offers pSOS support. TimeSys has joined the list of embedded Linux companies providing pSOS support, this time via a pSOS "abstraction layer" on top of their Linux distribution, TimeSys Linux/RT. They are using the RTAI (Real Time Application Interface) for their real-time Linux support. Section Editor: Liz Coolbaugh |
July 13, 2000
Please note that not every distribution will show up every week. Only distributions with recent news to report will be listed.
|
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Development page. |
Development projectsNews and EditorialsMicroprocessor development and Linux Linux has proven itself to be an excellent platform for developing code with many generic tools available for a wide variety of projects. The world of 4, 8, and 12 bit microprocessor development is an area that could benefit from a broader base of Linux tools. Currently, assemblers and disassemblers make up most of the free software for working with microprocessors. To date, there doesn't appear to be much support from the microprocessor manufacturers for Linux In Circuit Emulators (ICE) and EPROM/Microprocessor programmers. Perhaps some of the recent Linux activity in the embedded world will inspire these companies to start releasing their development tools under Linux. The Microchip PIC chips are now supported by the GPASM assembler. Paul Vollebregt's GnuPIC site lists a number of useful micro development tools, some of which are open-source. Speaking of PICs, take a look at the world's smallest web server which is claimed to fit into a matchbox. There are several free assemblers available for the Motorola Motorola 680X/6811 series chips. Mozilla Status July 6, 2000. The latest Mozilla Status Update is out. Work on Mozilla involving Tru64, XML, DOM, LDAP, XPToolkit, and Composer are discussed. Mozilla Developer Meeting Aug 18. Alphanumerica will be sponsoring the Second Mozilla Developer Meeting on Aug 18 at the Netscape campus in Mountain View, California. Alphanumerica has created a mailing list for the event. The meeting will be held just after the Linux World Expo in San Jose. DatabasesPostgreSQL v7.0.2 Released . The PostgreSQL Global Development Group has released PostgreSQL v7.0.2. This is a bug fix release for v7.0 and v7.0.1, improved documentation is included. ElectronicsGeda Snapshot for July 4, 2000. The Geda project has released a new snapshot of it's electronics design and analysys tools. New versions of gschem and gnetlist are included along with improved documentation and more symbol libraries. InteroperabilityWine Weekly News for July 10. This week's Wine Weekly News is out. Numerous bug fixes are mentioned, but the main item of interest is an announcement from Corel that, now that PHOTO-PAINT is released, the company plans to merge all of its WINE work back into the project's tree and work more closely with the WINE project in the future. Corel also plans to help bring about the long-awaited WINE 1.0 release. Common threads: Introduction to Samba, Part 2 (IBM). Daniel Robbins of IBM's Developer Works has published the second article in a three part series on Samba. This article covers installation and basic configuration of Samba and is an easy introduction to this useful system. Network ManagementOpenNMS Update Volume 1.16. The latest OpenNMS Update has been released. Current code work involves an Event Subsystem, ICMPD in Perl, a Service Control Manager, and capsd. Office ApplicationsEvolution 0.2. Right on the heels of Evolution 0.1 comes Evolution 0.2, which integrates the Gnome mailer, calendar, and address book. Many new features are currently being added. Resynthesizer 0.2 for Gimp. Paul Harrison has written Resynthesizer , a plug-in for Gimp 1.1. Resynthesizer may be used to combine the texture from one image with another image. Killustrator Review (ShowMeLinux). Geno Boba from Show Me Linux has reviewed Killustrator, A KDE based drawing program. "Once the program is running, it's a fun ride, with a very shallow learning curve, but that's not because there's nothing to it. Modeled in the tradition of Adobe Illustrator and Corel Draw, KIllustrator uses a similar intuitive approach, choosing the simpler of the two when there's a choice between Adobe's working environment, and Corel's. Gotta hand it to these guys, they know a good thing when they see it in another program." On the DesktopKDE 2.0 Release Plan. The latest release plan for KDE version 2.0 has been published. The Feature Freeze is coming soon and KDE 2.0 is scheduled for release in 8 weeks. KDE History (Linux Planet). Linux Planet has published an article on the History of KDE. "I don't mean easy to use by Linux standards, either: I mean flat-out easy. You could poke around and figure out just about everything. As you got more familiar with KDE, deeper levels of configuration and customization were apparent. These guys, it seemed, had thought of pretty much everything." PalmtopsMicrowindows v0.88 adds far-eastern language support. The Microwindows project has added support for far-eastern languages. Microwindows is an open-source environment that competes with Microsoft's WinCE platform on palmtop platforms. Real-Time SystemsSecond Workshop on Real Time Linux Nov, 2000. The Thinking Nerds has announced the second Workshop on Real Time Linux, November 27-28, 2000 in Orlando, Florida. There is currently an open call for papers for this conference. Team takes different path to real-time Linux (EE Times). EE Times has run an article on Real Time Linux with comments from Victor Yodaiken, the developer of RT Linux. "With RTLinux on an X86 platform, interrupt handlers can spring into action within 15 microseconds of the detection of a hardware interrupt, compared with 600 microseconds for standard Linux. That time window is actually determined by hardware and will improve as processors get faster, Yodaiken said. " ScienceDocScope. Minoru Development Corporation has announced DocScope , an open-source project that uses XML to work with medical records. "DocScope will be a free medical information tool that is as natural and easy for physicians to use as the spreadsheet is for accountants." TelecommunicationSpeech based web initiative. SpeechWorks International, Inc has announced its plans to build a speech based implementation of the world wide web. The project will be based on the open-source Carnegie Mellon University SPHINX speech recognition software. Web-site DevelopmentZope 2.2.0 beta 4 released. The fourth beta for Zope 2.2.0 has been released. This is expected to be the last beta before the final 2.2.0 release. Zope Weekly News for July 7, 2000. The July 7 edition of the Zope Weekly News is out. Items discussed are the upcoming open source conference, the help system, and documentation. XML Standards Move Forward (InternetNews). InternetNews published this brief article mentioning that the XML Linking Working Group released its recommendation for the XML Linking Language (XLink) Version 1.0. Comments are being accepted until October 3rd. "'The Working Group is asking developers to look at the document, experiment and give us feedback,' Daly said. 'We are also hoping to see open source implementation, which is important for the success of a specification.'" Section Editor: Forrest Cook |
July 13, 2000
|
|
|
Development toolsErlangSixth International Erlang/OTP User Conference. The Sixth International Erlang/OTP User Conference will be held in Stockholm, Sweden on October 3, 2000. The conference is divided into two parts, applications and technology development. HaskellGlasgow Haskell Compiler version 4.08 released. A new release of the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC), version 4.08 was announced on Friday. Jens-Ulrik Petersen reported, "Apart from loads of bug fixes, the main changes include: a new improved profiling subsystem, fixed x86 native code generator, implicit parameters, and a new package system for libraries". For more details, check the release notes. PerlPerl 5 Porters summary for July 9, 2000. This week's Perl 5 Porters summary is out. A bug database system and the perl man page table of contents generator, buildtoc are discussed. Camp Camel. This Year's Camp Camel Perl campout is scheduled for September 7 through 10 in Weyehaeuser Wisconsin. It sounds like a wild time: "Also, bring things to shoot! Like AOL and MSN CD's or old computer hardware!!!!" Return of Program Repair Shop and Red Flags. Mark-Jason Dominus has written this article on cleaning up and optimizing a perl program. It is a good read if you want to see how an expert perl programmer deconstructs a program. PythonJuly 10 Python-URL. Here is Dr. Dobb's Python-URL for July 10. It covers the renaming of the 1.6 release (to Python 2.0) and numerous other topics of interest to the Python development community. Also note that the new Python release will be delayed, for the ominous reason that "a number of issues have arisen that CNRI and BeOpen are in the process of working out." Developing Gnome Application with Python (Linux Focus). Hilaire Fernandez of Linux Focus has written the first article in a series about Developing Gnome Application with Python. This is an extensive article that describes the building of a GUI based kid's game program. Five Minutes to a Python CGI(Webreview.com). David Mertz has written a nice article on writing CGI scripts in Python. " Compared to Perl, most people find Python code easier to read and maintain. Compared to VBScript or ColdFusion, Python packs more powerful basic constructs. Compared to PHP, TCL, or REXX (or C for that matter), it's a lot easier to make modular and object-oriented code in Python. Compared to JSP, Python is concise, dynamic, and loosely typed-in short, a lot quicker to develop. Compared to Bash...well. " Section Editor: Forrest Cook |
Language Links Erlang Guile Haskell Blackdown.org IBM Java Zone Perl News PHP Daily Python-URL Python.org JPython Smalltalk |
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Commerce page. |
Linux and BusinessLet's Make a Deal. One way to get your software out to a wider audience is to bundle it with other packages. This week we saw a number of deals of this sort. For example, Loki Software announced that they are now shipping PowerPlant, a suite of developer tools and software for Linux from theKompany.com. Loki mostly sells computer games, ported to Linux. theKompany.com has tools that help game developers. It's a win-win situation for both companies and their customers. Along the same lines, Corel has announced a deal which will get Corel Linux and Word Perfect Office 2000 bundled with systems sold by Andara Technologies. Sun Microsystems is doing it too. They announced a long list of companies that have agreed to redistribute StarOffice 5.2. The list includes Caldera, Red Hat, TurboLinux, SuSE, MandrakeSoft, Conectiva, Definite Software, Stormix, MacMillan, and Easy Information Technology. Lineo's product is its Embedix embeddable distribution and they are working with Hitachi Semiconductor to bring Embedix to Hitachi's SuperH processor. This deal between VistaSource (part of Applix) and Comdisco offers Linux desktop systems, based on refurbished computers, with the intent of making a very low-cost system aimed at schools, non-profit organizations, and other budget-constrained customers. Services can be shared too, as we see in this announcement from NCR, saying that it will be offering support services for Red Hat's distribution. Also service-oriented is this press release announcing plans from Cendio Systems and Cell Network to offer new companies developing free software "a complete range of services to help them get their businesses up-and-running more quickly". Cendio will be offering a development platform while Cell Network offers business development services. New Products. Terra Soft Solutions has announced a demo of an 8-node, Apple G4 cluster running Terra Soft's Black Lab Linux at MacWorld. MSC Software has released MSC.Nastran DMP for Linux. Dubbed ''Supercomputing Without a Supercomputer'', MSC.Nastran is a package that has been used in the aerospace and automotive industries to distributing large simulation tasks amongst many PC computers. SolSoft has announced the release of its "Solsoft NSM" proxy firewall code as open source. A quick look at the associated web site shows that the GPL has been used to license the code. Popular Power, developers of commercial distributed computing software software package released in April, announced the availability of a Linux client for their software. "Once downloaded from www.popularpower.com, the Popular Power software operates in the background of Linux machines. When a PC is idle or has spare processing power, the program gets a small piece of a large computing task from the Popular Power server and returns results when complete. Popular Power's general-purpose commercial software differs from that of earlier, non-commercial efforts in its ability to execute different types of jobs, as opposed to single functions." An open source release of the client is promised for early next year. The software is envisioned for use in donating time for research projects or even potentially selling unused time to commercial companies at some point in the future. IBM has announced the availability of "WebSphere Homepage Builder" for Linux.
Napster Press Release. Napster has posted a press release with information from the legal brief they have filed. "First, the RIAA contends that Napster users are infringing. However, under the decision that protected the manufacturing of MP3 players, referred to as "the Diamond decision," and under the Federal statute called the "Audio Home Recording Act," (AHRA) consumers have an absolute right to create and transfer digital music for noncommercial purposes. And since its users are not directly infringing, Napster cannot be liable for contributory infringement." Sourceforge growth rate 23 percent per month. VA Linux released this press release indicating that new free software projects have been added to the Sourceforge repository at a growth rate of 23 percent per month. Recent high-recognition additions to Sourceforge include MySQL and XFree86. Press Releases:Open Source Products.
Commercial Products for Linux.
Products with Linux Versions.
Java Products.
Books and Training.
Partnerships.
Investments and Acquisitions.
Linux At Work.
Other.
Section Editor: Rebecca Sobol. |
July 13, 2000
|
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Linux in the news page. |
Linux in the NewsRecommended Reading. Tim O'Reilly writes about gated open source communities. "Perhaps the term "gated open source community" has some negative connotations, since it suggests exclusivity, but at bottom, all it means is enabling users of a particular piece of software to form their own private community for source code access and sharing. This is a very appealing scenario for vendors and customers alike. It's also a great set of training wheels for wider participation in more traditional, fully open source projects." Companies. Upside takes a look at PenguinRadio's recent influx of capital. "At least PenguinRadio seems to be weathering the recent market fluctuations better than most Linux-related startups. Last week the company announced what it called "an infusion of venture capital" from Internet Partnership Group, a London-based tech incubator." This NewsTraders article reports that International Data Group has filed to sell 213,195 shares of VA Linux common stock. Also from NewsTraders: Red Hat Inc. co-founder Marc Ewing filed to sell 500,000 of the company's common shares, according to this article. News.com reports on SCO's quarterly results. "Analysts note that SCO has been hurt by the arrival of Linux, a less expensive clone of versions of Unix such as SCO's UnixWare. SCO initially derided Linux, which like SCO's Unix, runs most often on Intel hardware. But SCO has since warmed up to the operating system." Products. ZDNet looks at Internet server appliances. "These machines share three characteristics: They often have an unusual design to differentiate them from typical PCs; they include Web, e-mail, File Transport Protocol (FTP) and local area network (LAN) server functions; and they do so in a single box that runs Linux or FreeBSD Unix, a low-cost Unix product." SecurityPortal's Kurt Seifried asks the question, "Why don't vendors ship the software they use themselves?". "Most Linux vendors ship the same general packages - Sendmail for SMTP mail services, WuFTPD for FTP, Telnet for remote access and so on. The kicker, though, is that most of these vendors use different software on their servers." Wizards of the Coast plans to release its new version of the popular role playing game "Dungeons & Dragons". "When the 3rd edition of D&D is released in August, Wizards plans to give the core rules for the game away for anyone to use and amend, hoping that when other companies publish games, whether they are supplements for the basic D&D game or new games entirely, it will lead gamers back into the fold." Business. Here's a lengthy introductory article in Colorado Biz. "So why Linux? Corporate customers are beginning to see Linux as an inexpensive fit for applications that run on their servers, especially those that run web sites, databases and e-mail systems. Linux is available at little or no cost and can be freely copied. Its reputation for reliability means it can take fewer people to troubleshoot a Linux system." There's also a quote from LWN editor Liz Coolbaugh. Here is an article about Linux's success in the recent SPECWeb99 benchmark. "To us at Signal Ground, the most interesting aspect of this benchmark was the SMP scalability of the Linux systems. 1, 2, and 4-processor Linux boxes earned scores of 1270, 2200, and 4200, respectively." ZDNet repeated the recent Netcraft results we mentioned in last week's LWN. "A real-time survey of Web servers revealed that in June the Apache Web server free software bundled with most Linux distributions has surpassed 10 million installations. That number far outstrips the 3.5 million installations of Microsoft's Web server software, according to the Internet consultancy Netcraft survey . The Apache software accounts for an increasing number of Web servers almost 63 percent in June while Microsoft's share of the market is decreasing." Then ZDNet put up this brief item claiming that the number of Linux-based web users is declining. "Up until April, the percentage of Web surfers using Linux rode a nice upswing, doubling from .16% in January of 1999 to .32% (see below). Since then, it has dropped to .27% as of last week, according to exclusive new data from WebSideStory's StatMarket." The New York Times takes a look at China's Linux policies. "'We don't want one company to monopolize the software market,' said Chen Chong, a deputy minister of information industries who oversees the computer industry in China. With Linux, 'we can control the security,' he added, so 'we can control our own destiny.'" (Thanks to Donald Braman and Dan Ginsberg) (The NY Times is a Registration Required site.) La Republica looks (in Italian) at Linux in China. "E' il software dall'anima più 'comunista' in circolazione e non sorprende che il governo cinese abbia deciso di adottarlo in massa." ("It's the most 'communist' in spirit software around and it's not surprising that the Chinese government has decided to adopt it massively"). English text is available via Babelfish. (Thanks to Massimo Marengo). ZDNet ran this article about Linux in handheld systems. "But it's not necessarily all about people who hate Microsoft. Linux developers said the hardware of Windows CE devices is more suitable for Linux, compared to the relatively lower processing power of current Palm devices. 'People are making business decisions about Linux,' said Jon Prial, director of marketing at IBM's Pervasive Computing division. 'It's a minority of the people who are doing this out of anti-Microsoft sentiment.'" InternetWeek looks at the list of companies considered "Microsoft Partners", such as Intel, Dell, Compaq, etc., and how many of them are hedging their bets with Linux. "'It's a wide open operating system war,' said Gartner Group Linux analyst George Weiss. 'They don't want to be tied to a single operating system.'". Upside examines the affect of the Microsoft break-up on Linux. "Only two things prevent future "Baby Bills" from taking over the Linux market, Kusnetzky says. The first is the outcome of the current Microsoft appeal, which even if unsuccessful, would provide enough of a delay for current Linux distributors to build their own connections." Licenses and Patents. ZDNet looks at alternative operating systems. "Will the Plan 9 bunny become as popular as the Linux penguin or the BSD deamon? I don't know, but it's cute enough to have its place among the other mascots." Here's an Upside article on software patents. "As for community-owned technologies such as Linux and Apache, [Ray] Alderman sees them as the wild card that makes the embedded systems market a particularly scary environment over the next five years. Although companies seem to accept the conditions of things like the General Public License (GNU), such conditions do not protect the underlying source code from patent claims." Resources.
The July issue
of LinuxFocus magazine has been announced (English version). Translation into other languages is on-going.
LinuxOrbit tries to install Linux on a laptop. "I wasted a couple of hours hunting down the fixes for the SuSE 6.3 install, and feel like given a little more time and effort, I could get it installed. But since I had Mandrake 7.1 available, I thought I'd let it have a shot. The Mandrake 7.1 install was about as smooth as I could hope for. No problems encountered and the last step of the install was configuring X, which was also flawless. Very impressive. "
LinuxPapers
discusses configuration files. "Linux is famous for being
'hard to configure.' Reviews. LinuxDevices took a look at the Indrema entertainment system. "Gildred and the other Indrema founders observed that there were lots of innovations taking place for PC-based games, but not much for consumer game consoles, due to high barriers to entry for individual developers that kept them from breaking into the console market. So, they resolved to create a new game console. One designed, from the ground up, to provide a game development environment and infrastructure capable of enabling any level of developer -- from an individual to a large corporation -- to bring products to market easily, and without huge barriers to entry. And they decided that the keys to accomplishing this mission would be open source software, open APIs, and the Linux operating system." The Duke of URL has a new review of XFree86 4.0.1. The review includes benchmarks, and overview, and the latest NVidia drivers, version 0.9-4. IBM's DeveloperWorks site has posted this paper comparing Linux and NT in the server role. "Linux will soon surpass NT in most if not all network service applications. It is an open source, multi-vendor, and multi-platform server operating system solution. It is stable, versatile, and powerful, and it can be free. Anything Windows NT can do, it can do as well and often better; and the Justice Department is not trying to break up any Linux shops." Tucows has run this opinion piece claiming that Linux software companies are buying good reviews with free (as in "no charge") software. "A good example of this is the new version of Mandrake that recently came out. The reviews on it were great, so great in fact, that no one mentioned anything about the down side. Now, it is a great OS for Linux, and I will be the first to tell you that, but it also has some software conflicts and bugs that were never reported in most reviews. I spoke with some of the people who wrote reviews on Mandrake and they said that they don't like writing negative things because they get all this software free from Mandrake." ZDNet reports on Chad Simonds' Tucows article on Linux software reviews. "While some will find such claims shocking, journalists are all too familiar with such attempts to manipulate reviews. 'This is an endemic problem with publications that don't pay their writers,' claims one editor. 'You get what you pay for. And, when the only 'pay' is coming from the vendor, well what do you expect?'" Section Editor: Rebecca Sobol |
July 13, 2000 |
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Announcements page. |
AnnouncementsResourcesCreating Filesystems (LinuxNewbie.org). LinuxNewbie.org has made available this "newbieized help file" on creating filesystems and swap partitions. "The '-f' option should probably be avoided, unless of course you know what you are doing (but if you are reading this NHF, the chances that you do are not real high)." Embedded Linux Update for July 6, 2000. LinuxDevices.com has this listing of stories they have run over the past week. Many of them have already appeared in the pages of LWN, but if you are looking for news about embedded Linux, check it out. EventsO'Reilly Network at the Open Source Conference. Whether you're attending O'Reilly's conference or not you can keep up through the O'Reilly Network. IDG to convene CEOs at LinuxWorld. IDG World Expo announced a "no-holds-barred" roundtable of top Linux executives at the upcoming LinuxWorld Conference & Expo. LinuxWorld will be held at the San Jose Convention Center, August 14-17, 2000. NLUUG Autumn Conference CFP. The Dutch Unix User Group (NLUUG) has put out a call for participation for those who would like to do a presentation or tutorial at the November 9 conference. Talks can be in either English or Dutch; the deadline is August 25. Web sitesSiliconPenguin.com launches. A new site called SiliconPenguin.com has announced its existence. It aims to be an embedded Linux portal. |
July 13, 2000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Software Announcements
|
Our software announcements are provided courtesy of FreshMeat
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sections: Main page Security Kernel Distributions Development Commerce Linux in the news Announcements Back page See also: last week's Back page page. |
Linux Links of the Week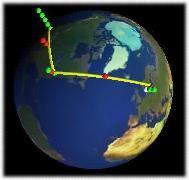 An Atlas of
Cyberspaces is a great resource for those interested in how the net is
put together. It's full of Internet maps, graphical route tracers (like xtraceroute, shown
here), and many, many other goodies.
An Atlas of
Cyberspaces is a great resource for those interested in how the net is
put together. It's full of Internet maps, graphical route tracers (like xtraceroute, shown
here), and many, many other goodies.
Haven't had enough licensing talk? SourceForge has set up a forum dedicated to the discussion of software licenses. Section Editor: Jon Corbet |
July 13, 2000 |
|
|
This week in historyTwo years ago (July 16, 1998 LWN), the KDE/GNOME flamewars may well have hit their peak. It was no fun. Because it is 100% Open Source, because it is technically quite good, and because of the wisdom of its development team, GNOME will become the standard GUI for Linux. A large portion of the free software community will simply not accept KDE because of the Qt license. The screaming notwithstanding, KDE 1.0 was released this week. The development kernel release was still 2.1.108. Much discussion occurred on troubles with the 2.1 memory management subsystem - a conversation which continues, with many of the same participants, to this day. The 2.0.35 stable kernel was released this week. The Debian 2.0 release was in its third beta, with only 39 release critical bugs left to be fixed. Transvirtual released Kaffe 1.0. And Netscape was proclaiming the success of the Mozilla project, with a Communicator 5.0 release expected by the end of the year. One year ago (July 15, 1999 LWN) was a relatively slow time in the Linux world. The development kernel was at 2.3.10. The allegedly stable kernel was 2.2.10, but the kernel hackers were working hard to be sure that a file corruption bug was truly stamped out before releasing 2.2.11. The Debian project, meanwhile, pondered freezing the 2.2 "potato" version, with talk of a possible release in September (of 1999!). A slightly different sort of endorsement came in this week: Once I explain what Linux is, I am certain you will understand why it is important for the Christian community of computer users to embrace it. More Internet sites use Linux on their servers than any other OS. Linux is revolutionizing the information technology (IT) universe just like the early Church changed the Roman Empire in the first century AD. | |
|
|
Letters to the editorLetters to the editor should be sent to letters@lwn.net. Preference will be given to letters which are short, to the point, and well written. If you want your email address "anti-spammed" in some way please be sure to let us know. We do not have a policy against anonymous letters, but we will be reluctant to include them. | |
Date: Thu, 6 Jul 2000 18:39:30 -0400 From: "Jay R. Ashworth" <jra@baylink.com> To: letters@lwn.net CC: torvalds@transmeta.com, risks@csl.sri.com Subject: Aw, shit. I've had to disagree with some impressive people in my time, but never with Linus Himself. :-) Last weeks' Linux Weekly News quotes Linus, from the Kernel mailing list <http://lwn.net/2000/0706/a/latencylinus.php3>, concerning a debate on Linux kernel latency (and realtime extensions): > Well, I personally would rather see that nobody ever needed RTlinux at > all. I think hard realtime is a waste of time, myself, and only to be used > for the case where the CPU speed is not overwhelmingly fast enough (and > these days, for most problems the CPU _is_ so overwhelmingly "fast enough" > that hard realtime should be a non-issue). If you want to assume that raw processor speed is enough to make (hard) real-time a "non-issue", you have to be willing to bet -- your life, because that's part of what hard real-time systems are all about -- that there is not *one line of code in your entire system* that can hang against real time running, keeping the machine from responding within the prescribed latency to an external stimulus. Nothing in the user apps. Nothing in the kernel. Nothing in the device drivers. That is a *LOT* of code to verify. Given the degree of complexity of today's instruction sets, I'm tempted to say it's not possible to do it. It's certainly a lot easier if all you have to validate is the Hard-RT kernel and the code you want to run. Yes, for soft-realtime, this approach ought to work nicely. But the hard-RT guys are solving a problem that differs not merely in degree, but in *kind*, even though it may appear to be merely a more stringent application. When that limit sensor on the robot arm that's about to pin you against the wall trips, you do *not* want a hard drive spin-up (or someone's bad code) to get you killed. (And yes, I realize that if you are working on life-safety type systems, you need to be evaluating every line of your code anyway; my point is that, if you can verify that the hard-RT kernel is the only part that needs to be validated, then that's all you need to check to that level of thoroughness -- and that's a *much* shorter code path, no?) Cheers, -- jra -- Jay R. Ashworth jra@baylink.com Member of the Technical Staff The Suncoast Freenet Tampa Bay, Florida http://baylink.pitas.com +1 727 804 5015 | ||
Date: Thu, 6 Jul 2000 17:22:39 -0700 (PDT) From: Linus Torvalds <torvalds@transmeta.com> To: "Jay R. Ashworth" <jra@baylink.com> Subject: Re: Aw, shit. On Thu, 6 Jul 2000, Jay R. Ashworth wrote: > > > [ Me quoted on not being all that excited about hard-realtime ] > > If you want to assume that raw processor speed is enough to make > (hard) real-time a "non-issue", you have to be willing to bet -- your > life, because that's part of what hard real-time systems are all about > -- that there is not *one line of code in your entire system* that can > hang against real time running, keeping the machine from responding > within the prescribed latency to an external stimulus. > > Nothing in the user apps. Nothing in the kernel. Nothing in the > device drivers. Hey. I write OS's for a living. If my _life_ depended on something specific having 5usec latencies, I'd prefer not to have a hard-RT OS under it at all. There are always bugs, and branding something "hard realtime" does not make those bugs go away. Look at QNX on Mars. Yes, it worked in the end, but that was a bug _due_ to trying to be real-time. It happens. Priority inversion. Programmer error. TLB and cache worst-case schenarios that nobody thought about and never got caught in testing. If you're _that_ latency-critical, I would suggest special hardware to do the latency-critical stuff, and running a specialized app on that hardware. I'd sure prefer not to use standard PC parts, thank you very much. Use a real OS on "regular" hardware for the non-critical stuff, like the pretty pictures to control and show what's going on. > Yes, for soft-realtime, this approach ought to work nicely. But the > hard-RT guys are solving a problem that differs not merely in > degree, but in *kind*, even though it may appear to be merely a more > stringent application. "My problems are so special that I can only run my own code". Sure. But if that's _really_ the case you'd better run it in memory that the "untrusted" OS cannot even touch. And on hardware that the untrusted OS has a hard time corrupting. Either it is critical or it isn't. If it's critical, you don't stop at the OS level, you go all the way. If it isn't, then you're a _lot_ better off usually just getting standard components and just stacking the hardware in your favour (ie "too much memory, too fast CPU, too fast disk, and to hell with hard real-time"). In short, I don't think there are all that many applications where "hard realtime" makes sense in a general-purpose OS. And it sure as hell should not be an interface that somebody doing streaming video and audio should _ever_ touch. Linus | ||
Date: Fri, 07 Jul 2000 00:55:24 +0800 From: Leon Brooks <leon@brooks.smileys.net> To: editor@lwn.net Subject: Defacing websites Last week's LWN covered an article which osOpinion was kind enough to publish for me (http://www.osopinion.com/Opinions/LeonBrooks/LeonBrooks5.html). Most of the feedback has been extremely positive, but I had one chap go off at me for advocating the defacement of websites. I do indeed advocate the defacement of a website in the article, but hasten to point out that it is at the invitation of the site's owner. The principle can be illustrated by a story about Tetzel. This enterprising lad, a member of the Papal Court, was out and about hawking indulgences for the benefit of the Holy Roman Spiritual Empire. An indulgence was (is) a document purporting to remit a particular sin or class of sin, past present _or_future_. "Father, forgive me, for I am about to sin?" "...for I am sinning?" Hmmm... very Microsoft... anyway, a gentleman bought an indulgence from Tetzel permitting him to indulge in armed robbery. As Tetzel subsequently left town with his (copious) ill-gotten gains, lo, who should step from the bushes armed and dangerous but our recently accredited highwayman - who promptly absconded with said ill-gotten gains. Tetzel then had the man arrested and brought to trial, at which trial the indulgence was produced. The judge asked Tetzel to verify that his signature and hence the indulgence behind it was valid. What was a man to do? There would have been dozens of spectators present who had purchased their own indulgences. Tetzel said yes, the judge said [klonk] case dismissed. Following the same principle, and bearing in mind his record, I advocate breaking John Teztel's, sorry Taschek's, hack-me site Windows system(s) if you're sure you can. After all, he asked you to. Just be careful to make the fact public and obvious. And if you can't surely break them, avoid his site and get on with something useful. -- Linux will not get in the door by simply mentioning it... it must win by proving itself superior. We have no marketing department, our sales department is an FTP server in North Carolina and our programming department spans 7 continents. Am I getting through? -- Signal11 (/.) | ||